The Basics of Blood Pressure
Your blood pressure reading has 2 numbers. The top number is called systolic blood pressure. It is the pressure when the heart squeezes to pump blood to the rest of the body. The second, or bottom number, is known as diastolic blood pressure. It occurs when the heart relaxes.
Blood Pressure
Your goal for blood pressure is less than 120 and less than 80. If you have diabetes or kidney problems, your nurse or doctor may have a different goal for you.
Always contact your nurse or doctor if your systolic—top—pressure is above 180 or your diastolic—bottom—pressure is above 110.
Check Your Blood Pressure Numbers at Home
Checking your blood pressure at home will help your nurse or doctor or nurse know if your numbers are normal or high. Ask your doctor or nurse to help you find the correct size home blood pressure cuff and quality monitor. Do not use finger or wrist monitors.
Learn more about checking your blood pressure at home.
How to Lower Your Blood Pressure
- Aim for 30-60 minutes of activity each day. Learn more about exercise and blood pressure.
- Reach a healthy weight. Learn more about how to reach a healthy weight.
- Eat a healthy diet and eat less salt (sodium). Learn more about how to eat less salt.
You have the power to make changes to improve your health.
Learn About Your Medicines
- Most people with high blood pressure need at least two medicines to lower their blood pressure to a healthy level.
- Your doctor or nurse may need to change your medicines to find what works best for you. This is normal.
- If you don't feel well after taking medicine, call your doctor or nurse.
- Don't stop taking your medicine until you talk with your doctor or nurse.
Learn more about your blood pressure medicines
How does high blood pressure affect your body?
- Your Brain - High blood pressure hurts the arteries leading to the brain and increases your risk for stroke (brain attack).
- Your Heart and Blood Vessels - High blood pressure hurts your heart and blood vessels and increases your risk for heart attack.
- Your Kidneys - High blood pressure hurts your kidneys and increases your risk for kidney failure.
Blood Pressure Home Monitoring
Checking Your Blood Pressure at Home
Blood pressure numbers are often lower at home than in the clinic. The goal for blood pressure at home is less than 120 (systolic—top number) and less than 80 (diastolic—bottom number).
Choose A Blood Pressure Monitor
- Choose a good home blood pressure monitor by asking your nurse or doctor for advice or choose from a validated device.
- Bring your monitor to your next appointment so your nurse or doctor can
check the measurement. - Do not use a finger or wrist monitor.
- To find a cuff size that is right for you, measure the size of your upper arm with a tape measure.
- If you do not have a tape measure, you can use a piece of string or ribbonto measure around your arm, then compare the length of the string or ribbon to a ruler to see what size cuff you need.
- You can also print out a paper measuring tape (PDF).
When to Take Blood Pressure
- Wait for at least 30 minutes after drinking alcohol or caffeine, smoking or exercising before you take a reading.
- Rest for at least 5 minutes before you take a reading.
- Take your blood pressure twice a day for 7 days. The best time to take your blood pressure is in the morning (2-3 readings) before taking your medicines and in the evening. Each reading should be 2 minutes apart.
How to Take & Record Blood Pressure
- Sit with your legs uncrossed, your back supported and your feet on the floor.
- Rest your arm at heart level on a table.
- Measure your blood pressure in both arms the first time you use a monitor.
- Use the arm with the highest reading to take future readings.
- Use a log to record your readings or print the numbers stored on your monitor.
- Always take your log or bring your monitor with stored readings to show your doctor or nurse.
Blood Pressure and Exercise
Get More Exercise
Regular physical activity helps reduce your blood pressure. But it's normal for blood pressure to increase right after exercising. In order to get the most accurate reading, the best time to take your blood pressure is 30 minutes after exercising.
What Exercises Are Safe?
Always talk to your doctor or nurse before starting or changing your exercise routine to find out what exercises are safe for you.
Why Is Exercise Good for You?
Exercise helps prevent heart attack and stroke by:
- Lowering your blood pressure
- Increasing your HDL, the good cholesterol
- Controlling your blood sugar
- Helping you lose weight
- Reducing stress, depression, and anxiety
- Improving muscle strength, balance, and fitness
Exercise Tips
- Choose walking, biking, swimming, and dancing. These are all good exercises for the heart and blood pressure.
- Exercise at a moderate pace for 30-60 minutes a day. You should be able to talk while you exercise.
- Warm up and stretch before exercise. Start walking or biking slowly, then increase your pace.
- Cool down! Walk or bike slowly and stretch for at least 5 minutes after you exercise.
- You can do three 10-minute exercise sessions or two 15-minute sessions per day.
Stick With Your Exercise Program
- Set your alarm 15 minutes earlier and go out for a morning walk.
- Go for a 15-minute walk on your lunch break.
- Walk or ride bikes with family or friends after dinner.
- Join a gym or a group program.
Blood Pressure and Salt
Eat Less Salt
You can lower your blood pressure by losing weight or eating less salt, also called sodium. As part of a healthy eating pattern, the goal is less than 2,300 mg of sodium per day—about 1 teaspoon of salt. Ideal amount is less than 1,500 mg per day, especially if you have high blood pressure, are age 50 or older, or African American.
As you eat less salt, your taste will adjust to the lower levels. It may take time to reach your goal but cutting your daily salt intake by 1/2 teaspoon can improve your blood pressure and your heart health.
Most people get most of their sodium from packaged and restaurant foods.
Top 10 Sources of Sodium in American Diets
- bread and rolls
- cold cuts and cured meats
- pizza
- fresh and processed poultry
- soups
- sandwiches such as hot dogs, hamburgers and submarine sandwiches
- cheese
- pasta dishes such as lasagna, spaghetti and macaroni salad
- meat dishes including meatloaf, chili and stew
- snacks such as chips, pretzels, popcorn and crackers
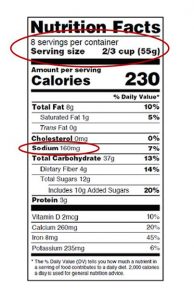
10 Easy Steps for Cutting Sodium
- Read nutrition labels for serving size and mg. of sodium. Choose foods with lower sodium.
- Prepare your own food when you can. Don't salt foods before or during cooking or eating.
- Add flavor without sodium. Use herbs and spices.
- Choose fresh or frozen meats instead of processed meats. Check to see if salt water or saline has been added.
- Use fresh, frozen, low sodium, or no-salt-added canned vegetables.
- Rinse canned foods such as tuna, vegetables, and beans to reduce sodium.
- Choose fat-free or low-fat milk and milk products in place of processed cheese products and spreads.
- Choose unsalted or low-sodium nuts, seeds, chips, and pretzels.
- Choose light or reduced-sodium ketchup, soy sauce, salad dressings, and seasonings.
- At restaurants, ask for your meal to be prepared without salt and with sauces and dressings served 'on the side.' Smaller serving sizes also mean less sodium.
Blood Pressure and Healthy Weight
Reach a Health Weight
When you choose healthy foods, you can help lower your blood pressure.
A Healthy Plate = A Healthy Weight
Balancing Calories
- Enjoy your food but eat less.
- Avoid oversized portions.
Foods to Increase
- Make half your plate vegetables and fruits.
- Make at least half your grains whole grains.
- Switch to fat-free or low-fat (1%) milk.
Foods to Limit
- Compare sodium in foods like soup, bread, and frozen meals and choose the foods with the lower amounts of sodium.
- Drink water instead of sugary drinks.
How to Create a Healthy Plate
View tips and sample meal plans at ChooseMyPlate.gov
Ways to Save 100 Calories
- Eat 1 cup of whole-grain cereal instead of 2.
- Add lettuce and tomato (instead of cheese) to your sandwich.
- Use fat-free salad dressing.
- Eat low-fat yogurt instead of toast and butter.
- Use mustard instead of mayo on sandwiches.
- Order thin crust instead of thick crust pizza.
- Eat whole fresh fruit instead of fruit juice.
- Use smaller bowls and plates for your food.
Tips for Losing Weight
- Count your calories, then eat 100 fewer calories a day.
- Walk 30-60 minutes most days of the week.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Eat smaller portions. The portion size for starch and protein should not be larger than a deck of cards.
- Fill up on salads and vegetables.
- Drink a large glass of water before your meal.
- Fill up on foods such as low-sodium soup.
- Keep a food diary to keep track of what you eat.
Blood Pressure Medicines
Most people with high blood pressure need at least 2 medicines to lower their blood pressure.
You and Your Medicines
- Know the name of each medicine you take.
- Carry a list of medicines with you.
- Know how and when to take each medicine.
- Know what side effects to report to your doctor or nurse.
- Tell your doctor or nurse about all of the vitamins, herbs, supplements, and pills you take.
- Never stop taking medicine without calling your doctor or nurse.
How Do Blood Pressure Medicines Work?
There are many medicines that lower blood pressure. They all work in different ways. Most medicines:
- Relax the arteries, or
- Remove extra fluid, or
- Allow your heart to beat more easily
Tips on Taking Your Medicines
- Use a weekly pillbox to help you remember to take your medicine, even if you only take one pill.
- Take your pills at the same time each day. Use a timer or alarm on your watch or phone to remind you to take your medicine.
- Write down on your calendar when you need to refill your medicine – at least 1-2 weeks before you run out.
- When you travel, carry your medicine list, and at least 1-2 days of extra medicine.
- Keep taking your medicines even if your blood pressure is at your goal.
Things to Talk About with Your Doctor or Nurse
- Ways to make your medicine schedule easier.
- A generic blood pressure medicine to help lower cost.
- If you don’t feel well after taking your medicine, call your doctor or nurse. Don’t just stop taking the medicine.
Disclaimer: While PCNA strives to provide reliable, up-to-date health information, this and other PCNA education materials are for informational purposes only and not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Only your healthcare provider can diagnose and treat a medical problem.
