What is Angina?
Nearly 10 million people in America have a heart condition called angina, and 500,000 more will develop angina each year.
Angina is the discomfort or pain you feel when your heart does not get enough oxygen. Angina usually occurs because the large arteries that carry blood and oxygen to your heart have become narrowed due to fatty deposits (called plaque or atherosclerosis). The fatty deposits build up over time on the inside walls of your arteries, causing the inside of your arteries to become smaller. When this happens, your arteries are not able to send enough oxygen-rich blood to meet your heart’s needs.
What Does Angina Feel Like?
Angina may not feel the same to all people. It can feel like:
- A crushing, heavy, tight or squeezing discomfort in the center of your chest
- Chest pressure or pain
- Discomfort or pain in your jaw, teeth, shoulder, or upper back
- Unusual shortness of breath
- Discomfort or pain down your arm that may make your arm feel numb
- A burning feeling under your breastbone (can feel like heartburn)
- Nausea or unusual tiredness
If you know how your angina feels, it will help you understand:
- What physical activities cause your angina
- If you get angina when you are stressed
- When to stop and rest
- When to take medicine like nitroglycerin to treat your angina
- When your angina gets worse or happens more often
- When to call your doctor or nurse about new, different, or worse
symptoms
To lower your risk, you can:
- Exercise at least 30 minutes, 5-6 days a week
- Eat a healthy diet
- If you are overweight, losing just 10 pounds may help your angina
- Stress less - Stress causes angina by making your heart work harder. Stress is a part of life, but you can learn to cope with yoga or meditation, exercise, adequate sleep, and doing more things that make you happy.
- Talk to your nurse or doctor if you need to lower your:
- cholesterol
- blood sugar
- triglycerides
- blood pressure
Your nurse or doctor can talk about medicines and other treatments that may be right for you.
Learn More
Angina Tests
When you see your nurse or doctor to have a test for angina,
you should explain:
- What your angina feels like
- What usually causes your angina
- How long it lasts
- How often you have angina
- What you do to make your angina go away
Along with this information, special tests will help your doctor or nurse decide the best treatment for you. Let them know if you have any questions about treatment options.
Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG)
A resting EKG is a “road map” of your heart and shows the heart’s electrical activity. An EKG can show if:
- You are having a heart attack or if you had a heart attack in the past
- Your heartbeat is regular or not regular
- Your heart is beating too fast or too slow
- The electrical activity is not normal
Exercise Test (Stress Test)
This test takes an EKG of your heart while you exercise, most often by walking on a treadmill. The treadmill slowly increases in speed and grade (like walking up a hill) to make your heart work harder. If your heart does not get enough oxygen during the test, you may have angina.
The exercise test tells you about:
- Changes in your heart rate and blood pressure
- Changes in your EKG while you exercise
- Any symptoms you may have with exercise
Your exercise test will help your doctor or nurse decide a safe level of exercise for you and if you will need other tests or treatments for your angina.
Echocardiogram (Echo)
An “Echo” is an ultrasound procedure that measures how well your heart is
working (pumping) and how well your heart valves are working. During the
“Echo” a monitor (transducer) is held over your heart to measure if your heart
is pumping normally and shows how your heart valves are working.
Cardiac Cath (Coronary Angiogram)
A cardiac cath is a very good way to see how blood flows to your heart. It usually
requires you to be in the hospital for 12 to 24 hours. A cardiologist threads a
small catheter (hollow tube) into your body through a large artery in your upper
leg or arm. When the catheter reaches your heart, the doctor injects a small
amount of dye into the heart’s arteries. X-rays are then taken to show the blood
flow to your heart. This test allows your doctor to see if the arteries going to your
heart are narrowed or blocked.
Nuclear Stress Test
This test uses X-rays and a nuclear tracer to create pictures of the blood flow to
your heart during an exercise test. If the blood flow to your heart is good, the
nuclear tracer shows up on the X-rays. If blood flow to certain areas of your
heart is poor because of narrowed arteries, the nuclear tracer will not show up.
If you can’t walk on a treadmill to take an exercise test, your doctor can use
another medicine to look at the blood flow to your heart.
New imaging tests for heart disease are being developed all the time. Your
healthcare provider may suggest a test not described here.
Learn More
Angina Treatments
Most of these medicines can be used alone or in combination to treat angina. You may be prescribed others if you have a stent. Make certain to take all medicines as you are told. Most medicines have few side effects. Talk to your doctor or nurse if you think you are having side effects.
Medicines for Angina
Beta-Blockers
Beta-blockers are used to treat angina and other health problems like high blood
pressure and abnormal heart rhythms. Beta-blockers cause your heart rate and
blood pressure to go down and reduce how hard your heart works.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium channel blockers help keep your arteries from getting tight or narrow. Some calcium channel blockers also lower blood pressure, which reduces how hard your heart works.
Late Sodium Channel Blocker
A late sodium channel blocker has been shown to be helpful in treating
angina. This medicine does not affect heart rate or blood pressure. It helps the heart relax between heartbeats, which improves blood flow to the heart.
Nitroglycerin
Nitroglycerin is a medicine used to improve blood flow to the heart. There are two different forms of nitroglycerin. Fast-acting nitroglycerin acts very quickly while long-acting nitroglycerin lasts for a longer period of time.
Fast-acting Nitroglycerin
Fast-acting nitroglycerin comes in two forms: a tablet or spray that goes under your tongue. Most people with angina should keep fast-acting nitroglycerin with them all the time. Fast-acting nitroglycerin quickly stops angina by causing blood vessels to relax and open up so more oxygen-rich blood flows to the heart.
When you begin to feel angina:
- Stop what you are doing, sit down and rest. If your angina does not quickly go away with rest, put one nitroglycerin tablet under your tongue or spray nitroglycerin under your tongue.
- Continue to rest until your angina goes away.
- If your angina is not better after 5 minutes of rest and taking nitroglycerin, call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room. You may be having a heart attack!
Long-acting Nitroglycerin
Long-acting nitroglycerin provides a small amount of nitroglycerin into your bloodstream all day. Many people take long-acting nitroglycerin so they have less angina during the day. Long-acting nitroglycerin comes in pills and skin patches.
You can take fast-acting nitroglycerin for angina even if you take long-acting nitroglycerin.
Nitroglycerin Tips
- Keep nitroglycerin in the original bottle it came in. Do not mix nitroglycerin in pill containers with your other medicines. If your bottle of nitroglycerin has cotton, throw the cotton away.
- Always have a fresh supply of nitroglycerin. Get a new bottle of nitroglycerin every 6 months. Nitroglycerin spray will last 2-3 years.
- Keep nitroglycerin at room temperature; don’t let it get too hot or too cold.
- Keep nitroglycerin with you at all times.
- When using a nitroglycerin skin patch or spray, follow your doctor or nurse’s instructions carefully.
- Medications to improve sexual performance in men can cause an unsafe drop in blood pressure when taken with nitroglycerin. These two medicines should not be taken in the same 24-hour period.
Other Treatments for Angina
Angioplasty and Stent
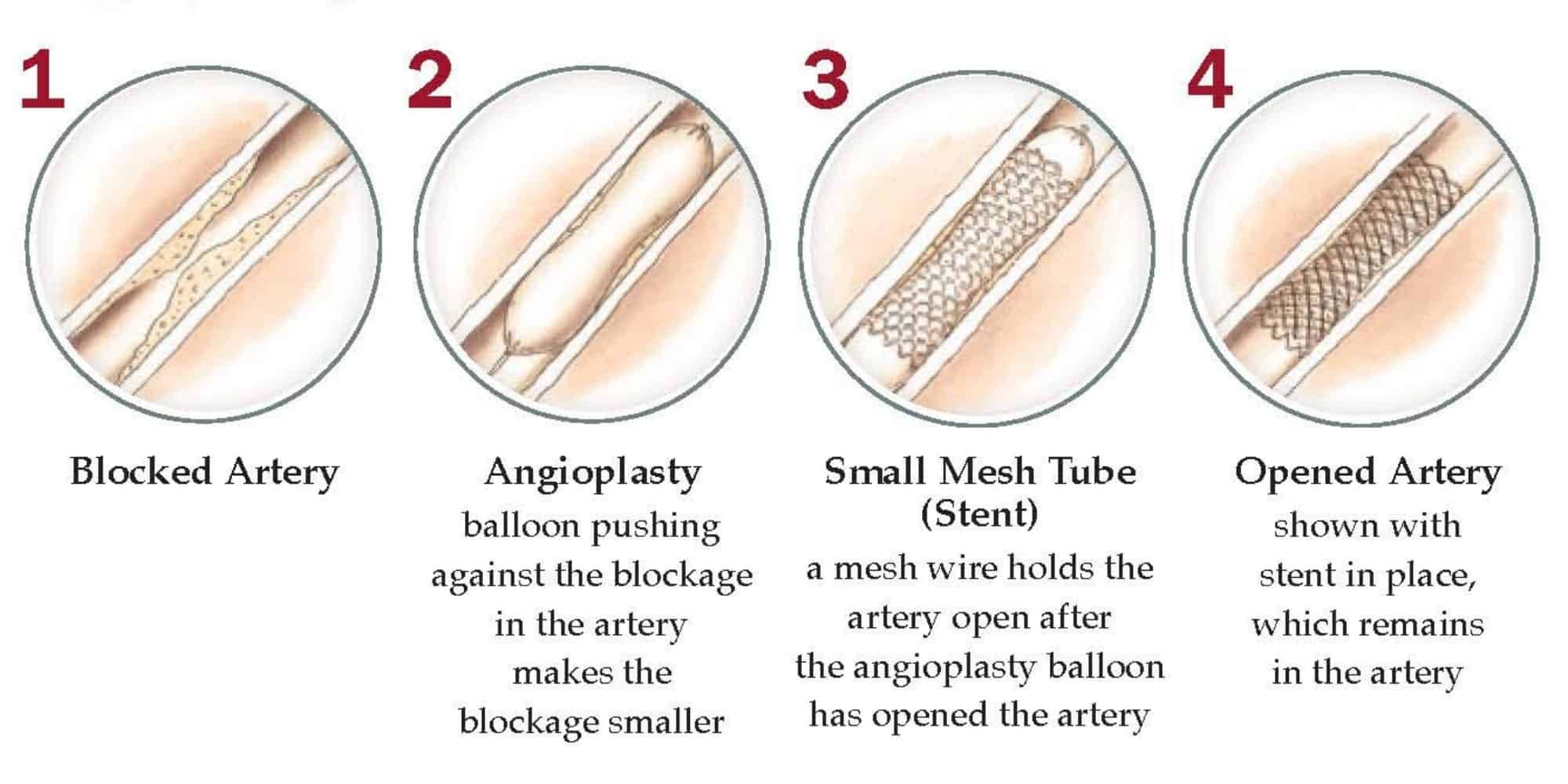
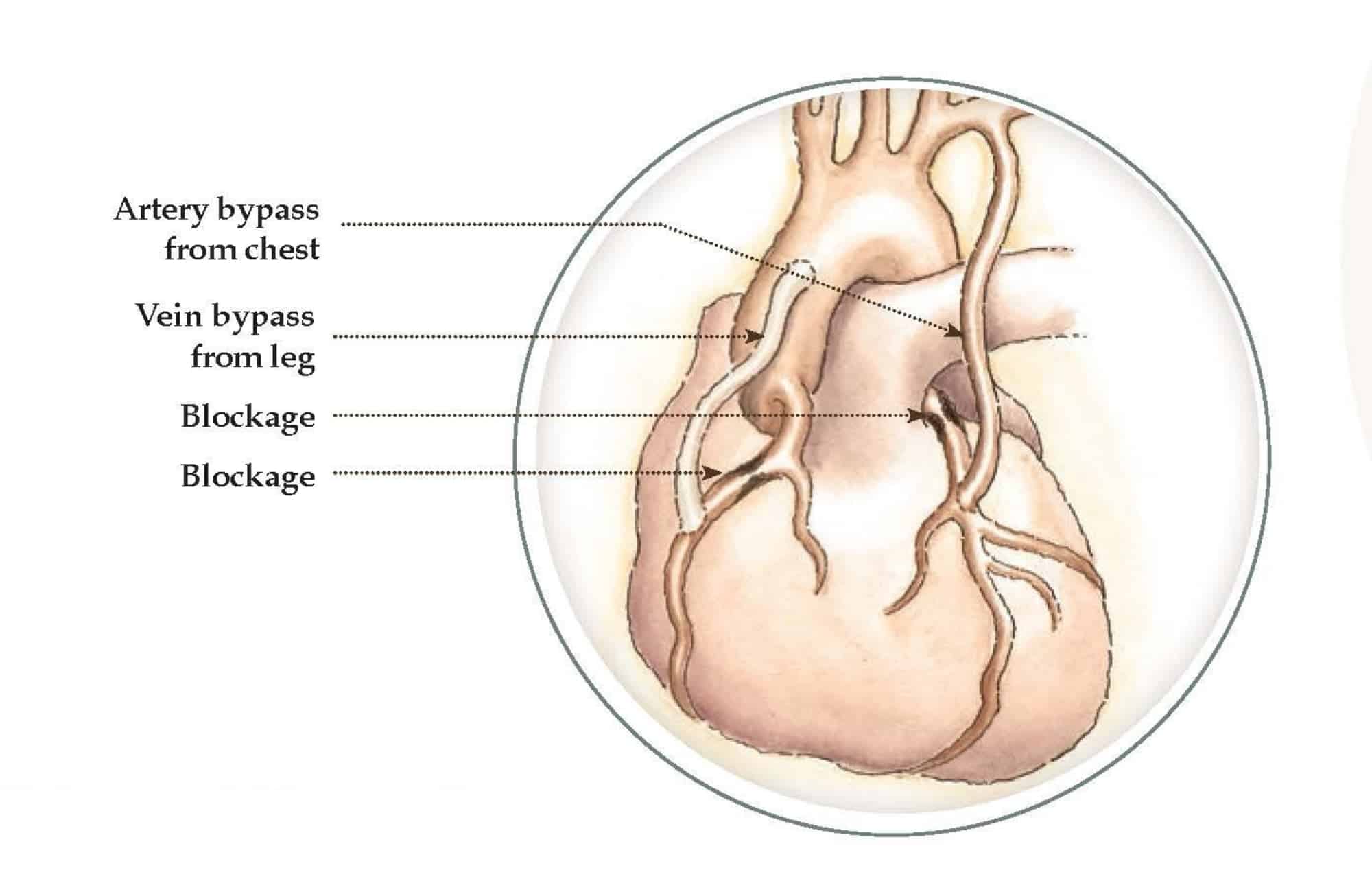
Heart Bypass Surgery
A bypass adds new blood vessels so blood goes around the blockage.
Enhanced External Counterpulsation or EECP
An EECP involves putting cuffs on the legs that repeatedly fill with air and then empty. This acts like a pump on the legs and helps fresh blood and oxygen get back to the heart. You will need a prescription for EECP. Talk to your doctor or nurse.
Learn More
Disclaimer: While PCNA strives to provide reliable, up-to-date health information, this and other PCNA education materials are for informational purposes only and not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Only your healthcare provider can diagnose and treat a medical problem.
